Autologous Fat Aspirate Grafting (AFG)
Autologous Fat Grafting (also known as Adipose Derived Stromal Vascular Stem cells Grafting) is used primarily for few reasons, one, when treating more advanced tendon, ligament or cartilage injury. Another reasons is that it provides a more condensed source of autologous reparative cells (adult cells from your own body), and also it acts as a matrix for cellular tissue and growth factors to slowly heal a defect. Adipose stem cells are one of the richest source of stem cells in the body. They have the ability to differentiate into chondrocytes, fibroblasts, and other musculoskeletal tissue. The adipose stem cells have very similar properties to bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, and have a wide range of therapeutic applications, based on its ability to self-renew and its ability to differentiate along multiple lineage pathways. AFG injections are used in cases of either more significant tears, defects, necrotic or avascular tissue, which may need new cellular material to be viable.
The abundance of signaling cells in adipose tissue and the ability to easily collect large amounts of adipose tissue via mini-liposuction presents as an advantage, and eliminates the need for tissue culturing. Depending on the literature reviewed, there is anywhere between 500 and 2500-times the number of reparative cells in adipose tissue as compared to bone marrow. The main components of the AFG fraction include adipose derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells, hematopoetic stem cells, adipocytes and attached progenitor cells, T regulatory cells and activated monocytes and perivascular cellular components.
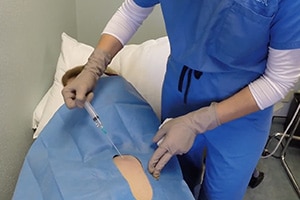
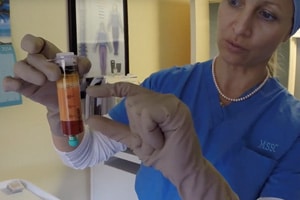
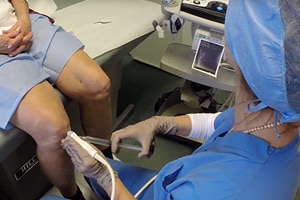
The AFG is obtained usually from the lateral hip, buttocks or abdominal area using a low suction system, as to keep the cells viable and undamaged. It is done under a local anesthetic. Usually no sedation is needed. The fat is obtained and the tissue is prepared, and mixed with platelet-rich plasma (PRP). The PRP is prepared by taking a tube of whole blood and processing it using one of the platelet harvesting systems. The fat is prepared and the platelet-rich plasma is added in appropriate quantities.
During the procedure the area of injury is examined and marked where the grafting will take place. Then this area is sterily prepped and locally anesthetized. Once the area is numb, the graft tissue is placed into the damaged area, until all the defects are filled with new tissue. Once this is accomplished, a sterile dressing is applied.
Usually there is some pain and discomfort for approximately 2-7 days. This tends to resolve with each day. Ice for 20 minutes, every 2 hours for the first day or so, is helpful. Appropriate pain medication might be used after the procedure, including Tylenol. Usually the patient receiving the graft would need to avoid NSAIDS for 5 days prior to the procedure and 5 days after the procedure. The patient should then follow-up in 4-6 weeks. Some patients may require physical therapy, depending on their situations. The graft grows and stays viable for 3 months, but may take up to 6-9 months to totally incorporate into the surrounding tissue.
Most recently AFG is being used in Regenerative Injection Therapy where it is injected into:
- Spinal joints and ligaments
To treat:
- Spinal joints arthritis
- Other spinal problems
After seeing a number of doctors without success, I saw Dr. Melnik. I had two PRP/stem cell shots in my back about three months apart and one in my knee. I have stopped all pain medication and am leading a very active life: going to the gym, walking, and playing golf. I recommend Dr. Melnik without hesitation.
